A proxy is an intermediary server that intervenes between you and your destination (for example a website) when you connect to the internet. The requests we make first go to the proxy, which forwards the request to the destination on your behalf and returns the response back to you. The most important feature is that this intermediary server can inspect, modify or block the content of your network traffic. It has more functions than the usual perception of hiding the IP address.
Proxies do not just forward data packets like a simple gateway, they understand the data at the application layer (e.g. HTTP requests).
Basic Proxy Types
Proxies are divided into basic types according to who they work for and for what purpose.
Forward Proxy
This proxy is the intermediary that the user (client) uses to access the internet.
Flow:You -> Proxy -> InternetPurpose: It is often used in companies or schools to filter and secure internet traffic and block access to certain sites.Feature: For it to work, the proxy settings must be set in the user's browser or operating system (Non-Transparent Proxy)
Transparent Proxy
It is a type of proxy that the user does not know exists and does not need to make any settings.
Purpose: It is often used by internet service providers (ISPs) to filter content without users' knowledge or for caching to load frequently visited sites faster.
Reverse Proxy
This proxy is a tool that the server uses to protect itself from the internet. It handles requests from the outside to the server.
Flow:Internet -> Proxy -> Your ServerPurpose: Protecting servers from DDos attacks, scanning incoming requests and blocking harmful ones (WAF - Web Application Firewall), load balancing.Example: Cloudflare
Let's Visualize with Burp Suite
Let's visualize what a proxy is by using the proxy inside BurpSuite.
- First let's open a default BurpSuite project and go to the top tabs
proxyand thenIntercept.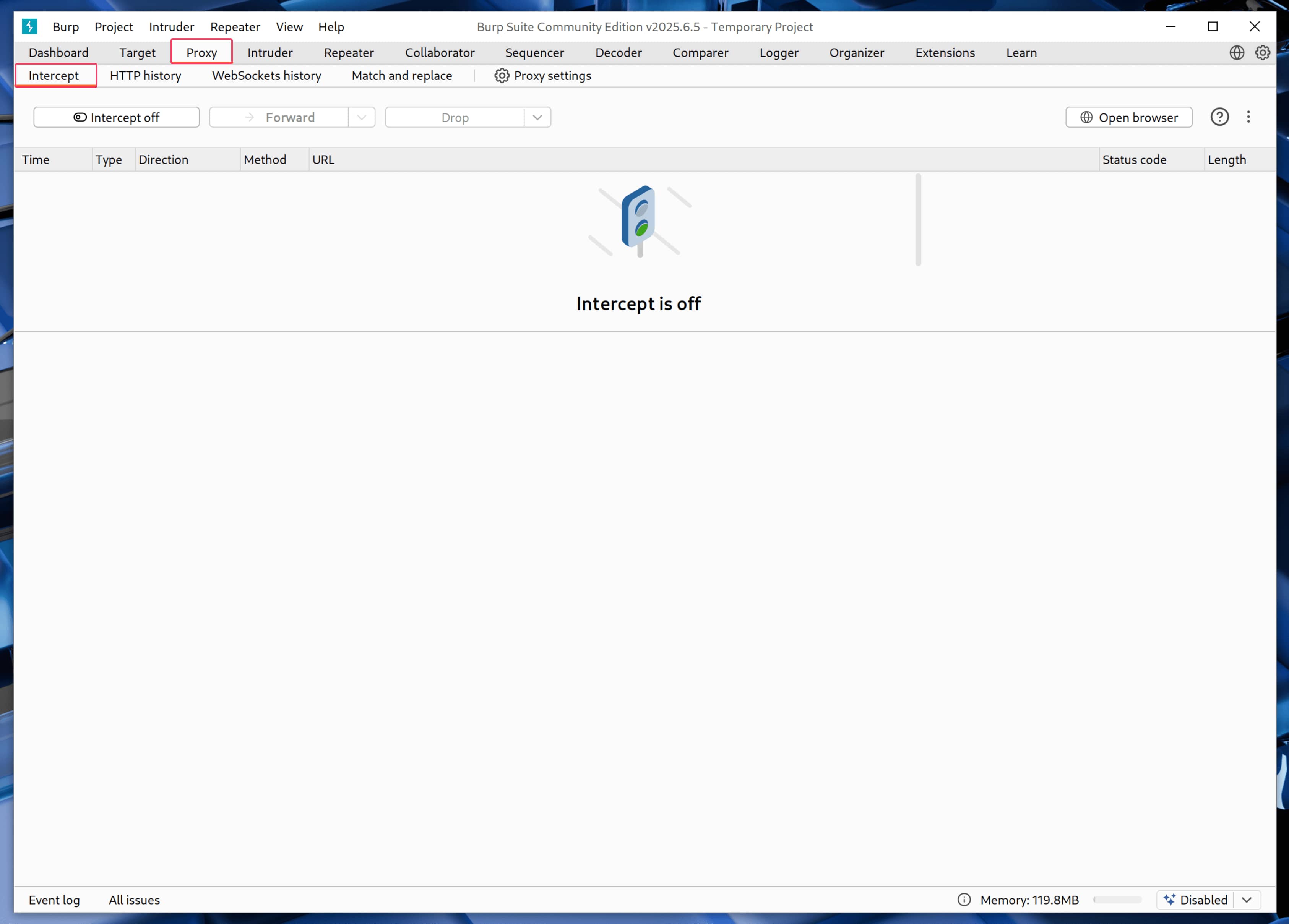
- Now let's open interception and then open browser to create a request. This will open the brupsuite browser which is already proxied.
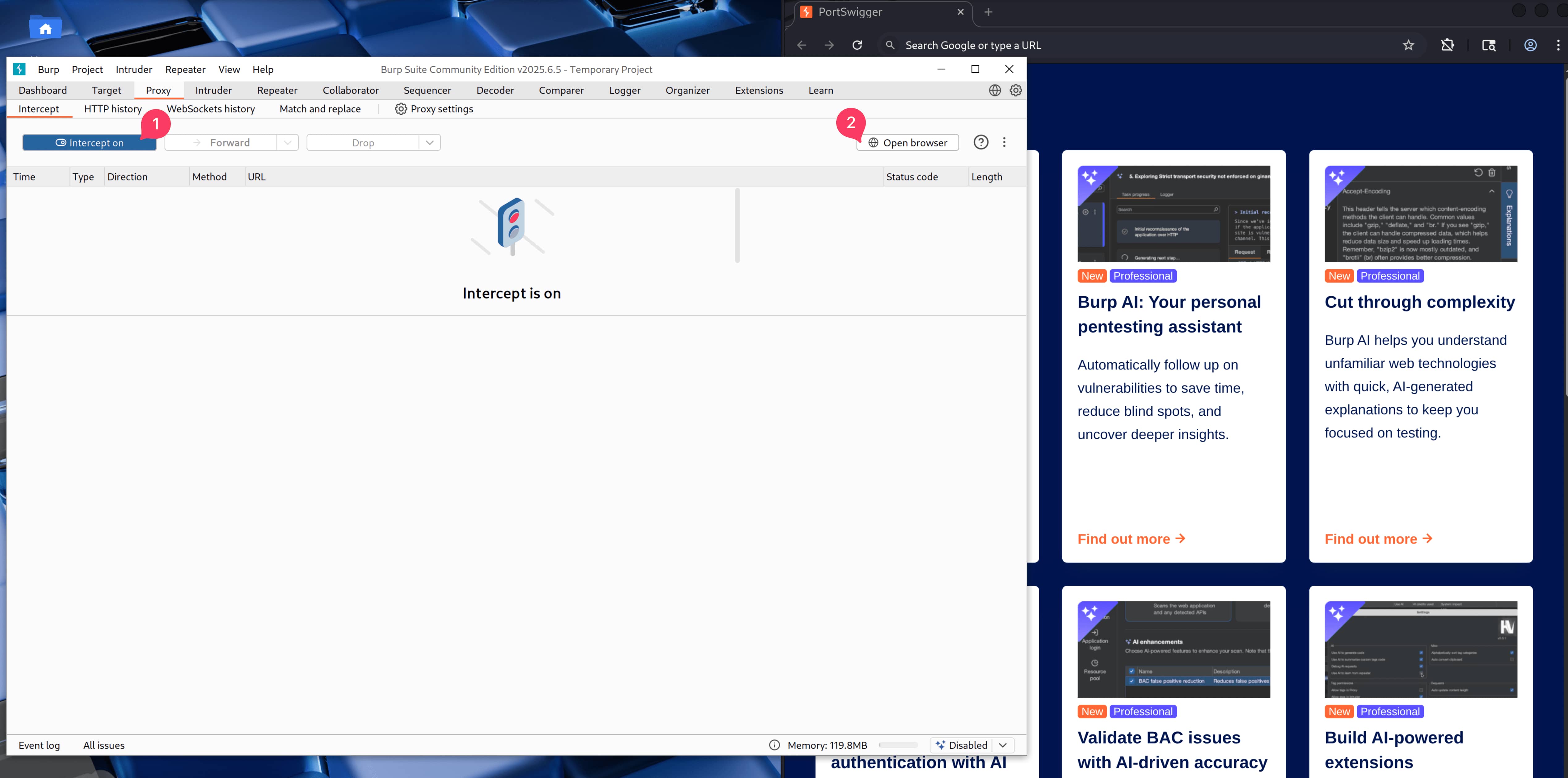
- Let's open a website in the browser, the goal is to create a request.
- Now if we look at our burpsuite screen, we can see the blocked requests and change them if we want.
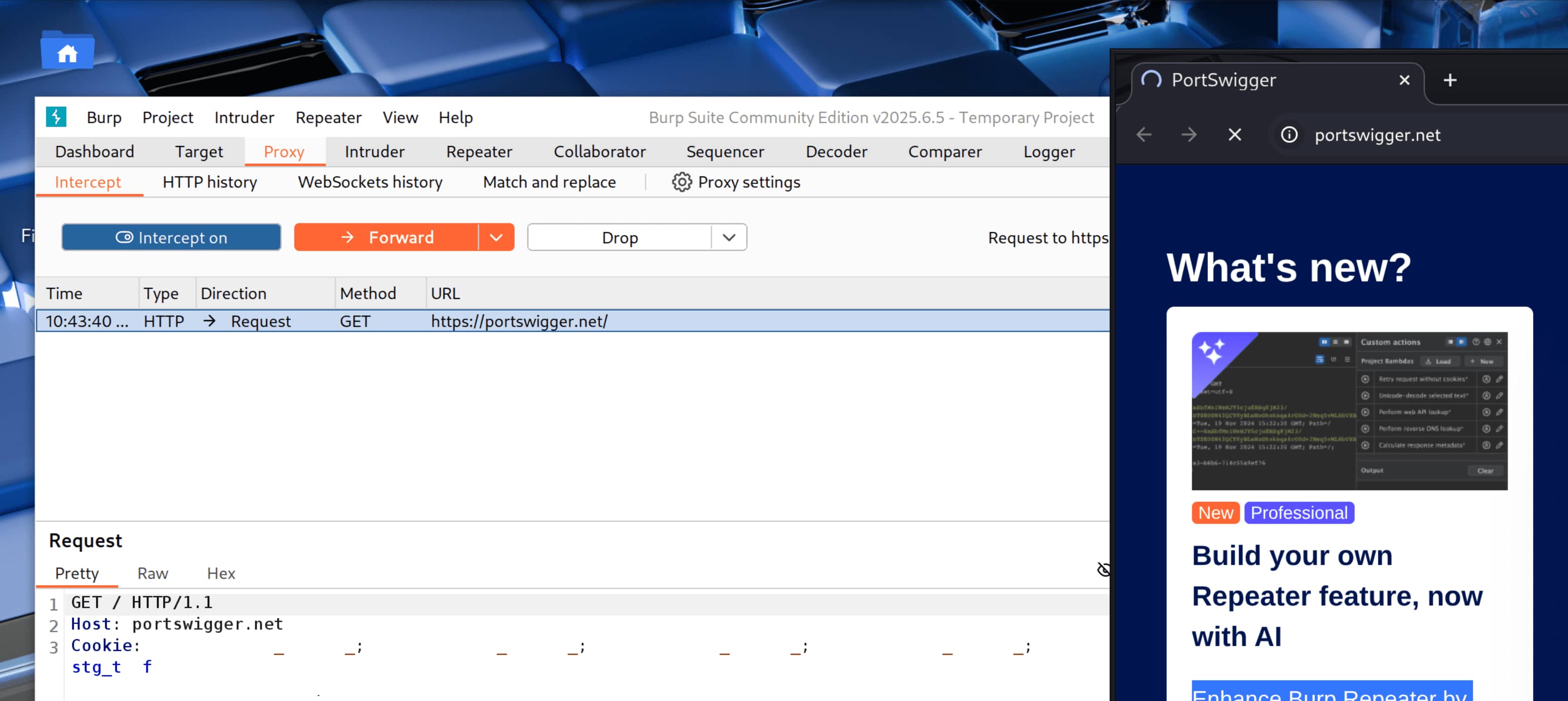
- As you can see, our requests are blocked and the page does not open. In this section, we can forward requests by saying forward or other operations.
As you can see, with BrupSuit's proxy we were able to intercept requests from the browser and inspect or modify them. This simple but effective step hopefully gave a better understanding of the concept of proxy.

Comments
Loading comments...